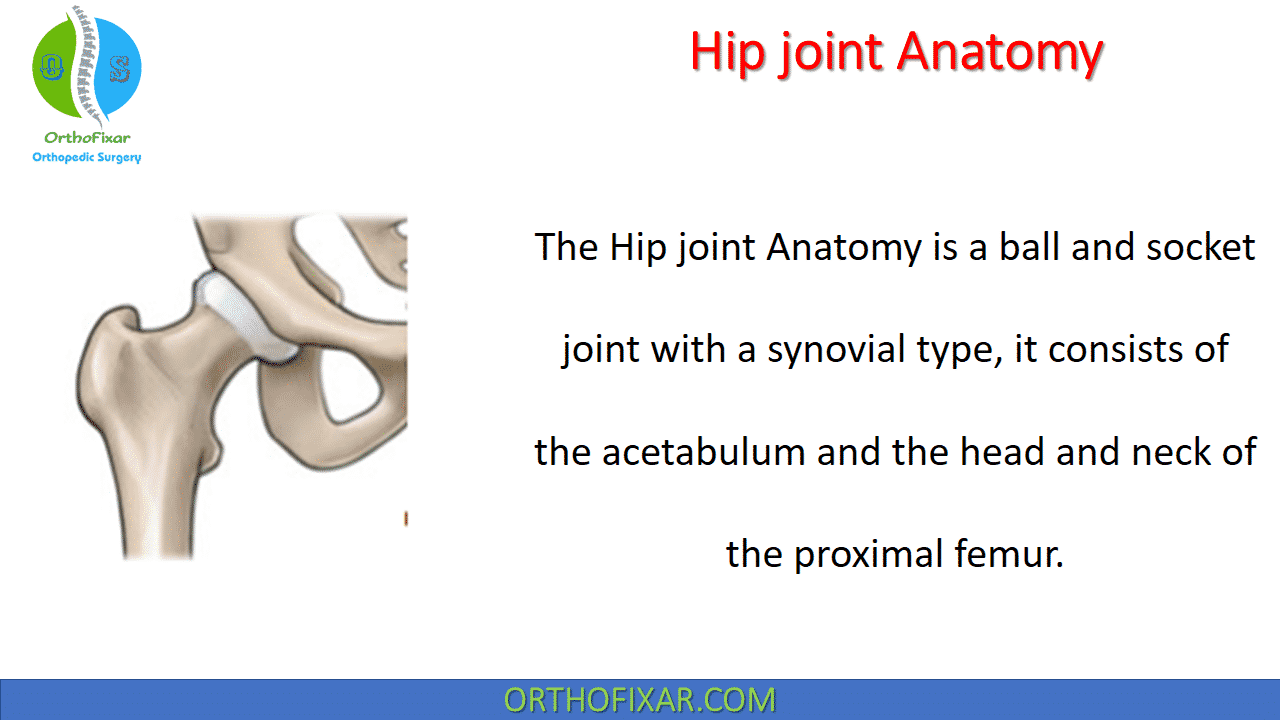
anatomi hip joint Biology Diagrams Learn about the hip joint, a ball and socket synovial joint formed by the acetabulum and the head of the femur. Find out its articulating surfaces, ligaments, neurovascular supply, stabilising factors and movements.

Learn about the hip joint, the second largest weight-bearing joint in the body, and its components. Find out how the femur, acetabulum, labrum, ligaments and muscles work together and what can go wrong with them.

Structure, Function, Anatomy, Location, Diagram Biology Diagrams
Hip Anatomy, Function and Common Problems Front View of the Hip Joint Bones. Normally, a smooth cushion of shiny white hyaline (or articular) cartilage about 1/4 inch thick covers the femoral head and the acetabulum.The articular cartilage is kept slick by fluid made in the synovial membrane (joint lining).

The main functions of the hip bone are to support the body's weight when standing and provide a base for leg movement. It connects to the spine at the sacroiliac joint and the leg at the hip joint. Hip bone anatomy comprises three parts that fuse during the teenage years: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. Ilium: The broad, upper part of the pelvis.

Hip joint: Bones, movements, muscles Biology Diagrams
Learn about the hip joint, a ball and socket synovial joint that connects the pelvic girdle to the lower limb. The hip joint is stable and allows a wide range of motion, but also has a complex anatomy with multiple ligaments and muscles.

Learn about the hip joint, a ball and socket joint that connects the femur and the pelvis. Find out its motions, stability, ligaments, labrum, nerves, blood supply and muscles.