Role of Mechanotransduction in Vascular Biology Biology Diagrams The mechanically activated cation channels PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 are crucial for mechanotransduction processes in mammals. This Review discusses the structural design and gating dynamics of PIEZO

Cellular mechanotransduction, a critical regulator of numerous biological processes, is the conversion from mechanical signals to biochemical signals regarding cell activities and metabolism.

Cellular mechanotransduction in health and diseases: from molecular ... Biology Diagrams
Living cells and tissues experience physical forces and chemical stimuli in a human body. The process of converting mechanical forces into biochemical activities and gene expression is mechanochemical transduction or mechanotransduction. Significant
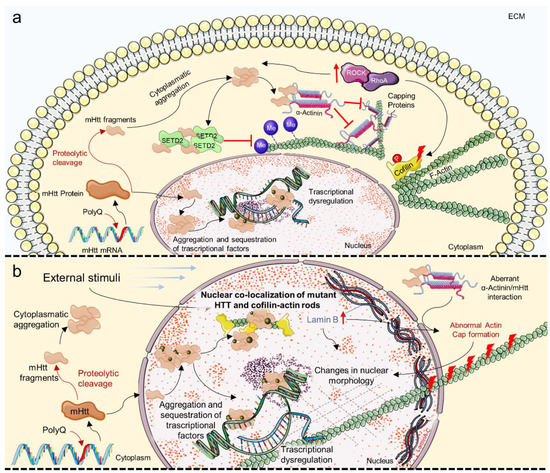
A great deal of this challenge arises from two crucial features of mechanotransduction: that cell and tissue structure both modulate and are sculpted by mechanical stresses, and that there are numerous feedback loops between cell signaling and force generation. (Kip1), and cell cycle progression in human capillary endothelial cells by cell

Mechanotransduction - a field pulling together? Biology Diagrams
Mechanotransduction is the ability of a cell to sense mechanical cues from its microenvironment and convert them into biochemical signals to elicit adaptive transcriptional and other cellular responses. Here, we describe recent advances in the field of mechanical regulation of transcription, highlight mechanical regulation of the epigenome as a key novel aspect of mechanotransduction, and RhoA signalling in fibrosis. A positive feed-forward cycle is illustrated. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) is released in response to tissue wounding. Severing the LINC complex, or complete removal of the nucleus, alter a cell's mechanotransduction. Much of the change may be due to reduced RhoA activity. The reason why RhoA activity
