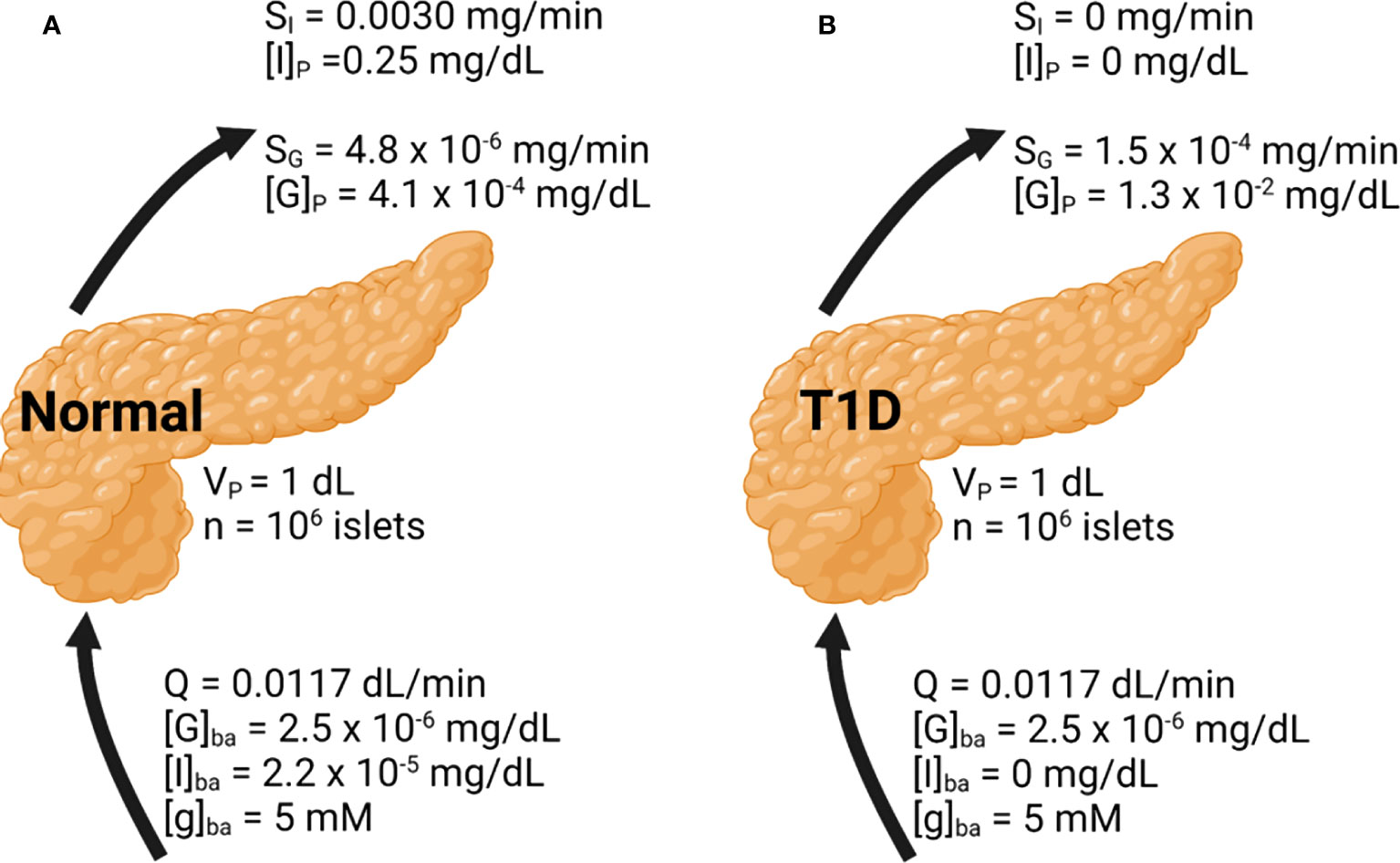
SU LMS Biology Diagrams Together, insulin and glucagon help maintain homeostasis, where conditions inside the body hold steady. When a person's blood sugar is too high, their pancreas secretes more insulin. When their Through its various hormones, particularly glucagon and insulin, the pancreas maintains blood glucose levels within a very narrow range of 4-6 m M. This preservation is accomplished by the
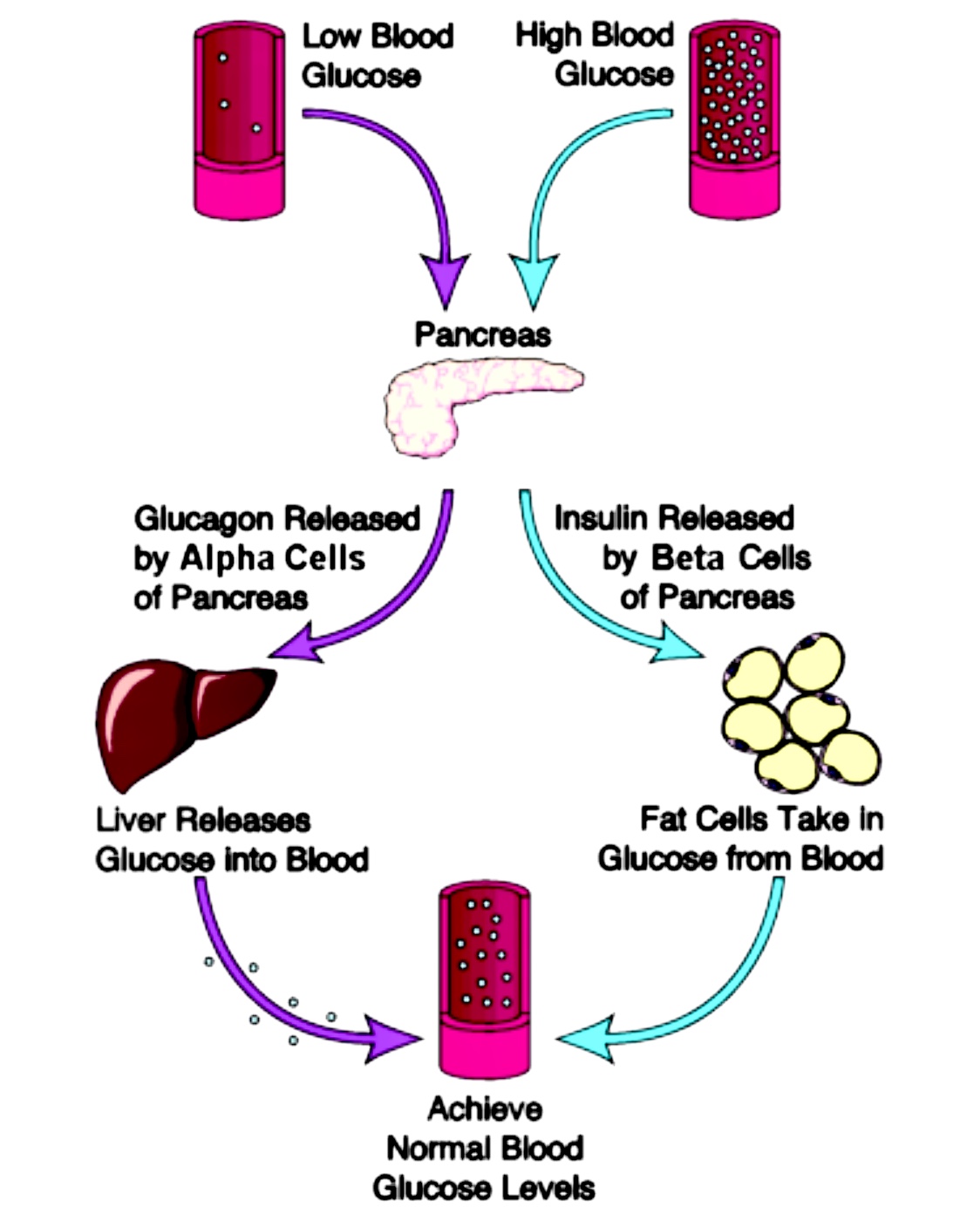
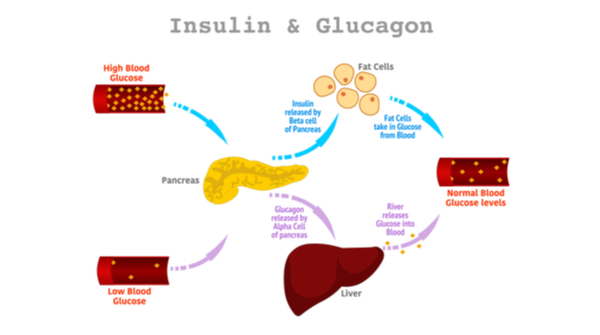
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, whereas insulin decreases them. 5 Somatostatin inhibits both, glucagon and insulin release, 6 whereas PP regulates the exocrine and endocrine secretion activity of the pancreas. 3, 7 Altogether, these hormones regulate glucose homeostasis in vertebrates, as described in more detail below. Although the
G6PC2 controls glucagon secretion by defining the set point for glucose ... Biology Diagrams
This review focuses upon the role of hormones secreted by the endocrine pancreas: hormones, which individually and collectively influence food intake, with an emphasis upon insulin, glucagon and amylin. Insulin and amylin are co-secreted by B-cells and provide a signal that reflects both circulating energy in the form of glucose and stored
+Insulin+Glucagon.jpg)
The pancreatic islets of Langerhans are central to fine-tuning metabolism to ensure metabolic homeostasis during the transition between fasting and feeding. Insulin and glucagon, the principal

Islet hormones at the intersection of glucose and amino acid ... Biology Diagrams
As mentioned above, pancreatic glucagon's metabolic functions are in many respects opposite to those of insulin. Glucagon's most prominent physiological role is to stimulate glucose production via hepatic glycogenenolysis or gluconeogensis, thereby helping maintain euglycemia during states of rapid glucose utilization or fasts, respectively.